Why 5800X Never Breaks 4.8GHz Single Core?-Common Causes and Fixes
Reviewed by: Amir Dylan
Fact Checked by: Tom David
Why 5800X Never Breaks 4.8GHz Single Core? This is one of the annoying problems that are common with any PC enthusiasts and gamers especially when they want to overclock their systems. Why this occurs is important to know because increasing the clock speeds can greatly influence your system’s performance in terms of gaming, work, and other tasks.
If your Ryzen 7 5800X is failing to get, or maintain, the boost clock that’s advertised, it can be for a few reasons. A single core boost clock of 8GHz, then you might not be utilizing your processor to the optimum level.
In the following article, I’ll discuss the possible causes for this problem, cite opinions of professional overclockers and specialists, and give you real-life tips and tools to optimize your Ryzen 7 5800X.
Whether you are trying to diagnose your current setup or attempting to fine-tune your setup even more this guide will provide you with the knowledge that you need to comprehend and deal with the clock speed issues regarding the 5800X.
Short Answer: Why 5800X Never Breaks 4.8GHz Single Core?
The Ryzen 7 5800X hardly ever maintains a 4. 8GHz clock speed on a single core because of the heat issues, power supply issues and how the AMD Precision Boost works.
Thus the CPU can momentarily go up to 4. 8GHz under the best conditions but due to conditions such as high temperatures in the range of 80-85°C, variation in power supply, and the type of workload, the clock speed tends to be fixed at 4. 6-4. 7GHz during sustained tasks.
This design is good in terms of performance and system stability but it also implies that 4. 8GHz is usually observed sporadically and not continuously for a long period of time.
Table: Compare Achievable Clock Speeds Across Various Cooling Solutions and Configurations
| Cooling Solution | Configuration | Average Achievable Clock Speed |
| Stock Air Cooler | Standard PBO Settings | 4.6GHz – 4.65GHz |
| High-End Air Cooler | Manual Overclock, Boost Disabled | 4.7GHz – 4.75GHz |
| 240mm AIO Liquid Cooler | Enhanced PBO, High Voltage | 4.7GHz – 4.78GHz |
| Custom Water Cooling Loop | Aggressive Manual Overclock | 4.75GHz – 4.8GHz (Brief Peaks) |
Expert Experience: Learning from the Overclockers
A lot of experienced overclockers have pointed out that it is quite possible to maintain a stable 4. 8GHz on the Ryzen 7 5800X needs more than just cooling but also the fine-tuning of the voltage and power settings on the BIOS.
For example, one of the experts learned that even with a water cooling system that was custom built, running four. 8GHz was difficult to maintain and would cause the device to spike for a couple seconds at a time.
Overclockers normally advise that one should shoot at a stable 4. It is important to strike a balance between the performance and stability of the system as well as its longevity and thus the new target is 7GHz.
Table of Contents
What Are the Common Causes of 5800X Failing to Maintain 4.8GHz?
The Ryzen 7 5800X can only rarely sustain a 4. 8GHz clock speed on a single core because of several interrelated factors, the main of them being thermal management, power delivery, and the nature of the Boost technology in AMD CPUs.
Thermal Throttling: The 5800X has been built with thermal safety in mind; if the temperature range is between 80-85°C, the CPU will downclock itself to prevent further rise in temperature. Despite having efficient cooling solutions, most of the users complain that their CPUs occasionally run at 4. 8GHz which becomes more realistic at about 4. 6-4. 7GHz during sustained workloads.

Power Delivery and Voltage Regulation: In order to achieve stable 4. 8GHz it needs stable power supply and good VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) on the motherboard. If the voltage is low or the VRM is loaded, the CPU will not be able to run at the higher clock speeds, it will usually settle at around 4. 65GHz because of lack of power supply which is a common problem with many chips in the market today.
Precision Boost 2 Limitations: Precision Boost 2 of AMD is a feature that allows the clock speed to increase depending on the current workload, temperature and power supply. Although, theoretically the CPU is capable of going up to 4. 8GHz, this peak is normally achieved in short spikes (less than 1 second) under lightly threaded conditions. In more intensive operations, Precision Boost will usually lock the frequency towards 4 GHz. 6-4. 7GHz to ensure that the system has the capacity to run efficiently and be stable at all times.
Video Guide
Personal User Experience: Examples from Forums and Discussions in Reddit
Many people at sites such as Overclock. net and Reddit have shared their challenges of sustaining 4. 8GHz on the Ryzen 7 5800X. A user said that even with a Noctua NH-D15 air cooler which is considered to be one of the best, their CPU was only able to touch 4. 8GHz during light workloads, but it went down to about 4GHz during the tests that were conducted on this laptop. 65GHz under heavy use such as gaming or video rendering.
One more Redditor with the custom loop water cooling said that they were able to sometimes boost up to 4. 8GHz, the clock speed would quickly return to 4GHz and that is the reason why the new processors have more cores. 7GHz because of the tendency of temperature rise during continuous usage of the CPU.
Note: If you’re experiencing high temperatures while troubleshooting clock speed issues, it’s essential to monitor idle temps as well. Issues with idle temps, especially with similar processors like the 5800X3D, can indicate broader cooling or power delivery problems that may affect overall performance.
How Does Thermal Throttling Impact Ryzen 5800X Performance?
Thermal throttling has a huge impact on the Ryzen 7 5800X as it reduces the clock speed in a bid to avoid overheating and this hampers the CPU’s ability to deliver optimal performance.
Temperature Thresholds and Throttling: The Ryzen 7 5800X comes with protection features that make it reduce clock speeds when temperatures go beyond 80-85°C.
In the case of heavy workloads, the CPU may first increase to the maximum speeds, but as the temperature rises, the processor will throttle down, and the clock speeds may drop to 4. 5-4. 7GHz to ensure that the operating conditions are safe for operation. This reduction can cause a degradation of the performance of up to 10-15% of its optimum level.
Impact on Multi-Core Performance: It is not just the single-core speeds that are affected by thermal throttling but even the multi-core speeds. For instance, if a user is running a video, or a game, the CPU might decide to throttle all the cores to keep the general temperature low.
For example, a user can have an all-core speed of 4 but find that this has been reduced to a certain degree. 5GHz to 4. 2GHz when thermal limit is crossed and hence, more time is taken to process and less frames per second.
Cumulative Effects Over Time: This is because, over time, thermal paste degrades, and cooling performance decreases, leading to more throttling at high temperatures. This can also affect the stability of the performance of the CPU and result in a progressive decline of the sustained clock rate, possibly stabilizing at 4. 2-4. 4GHz in intensive scenarios.
Note: If you’re experiencing issues with Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) settings not significantly affecting your Ryzen 5800X’s performance, it’s important to review your system’s power and thermal limits. PBO can be influenced by factors like cooling efficiency and motherboard VRM quality, which might be preventing the CPU from reaching its full potential.
Helpful Resources: Software and Hardware for Measuring the CPU Temperature and Limiting
HWMonitor: A full-fledged utility for tracking the CPU temperature, voltage, and power consumption in real time.
Ryzen Master: AMD’s official tool for controlling the performance and thermal parameters of the processors.
Core Temp: A small utility that monitors the temperature and the loading of the CPU for each core.
Expert Experience: Dealing with Thermal Problems
Experts suggest several strategies to mitigate thermal throttling on the Ryzen 7 5800X:
Upgrade Cooling Solutions: High-performance air coolers include the Noctua NH-D15 and 240mm or larger AIO liquid cooler should be used. The users have said that with enhanced cooling, the peak temperatures decrease by up to 10°C, which in turn allows the higher clocks to be sustained for longer time.
Optimize Airflow: Make sure your case has good air flow with at least two intake fans and two exhaust fans. Optimizing the airflow can decrease internal temperature by 5-10 degrees Celsius, which will help in avoiding thermal throttling.
Undervolting: It is possible to under voltage the CPU so that it produces less heat while still delivering the same performance. This technique can reduce temperatures by 5-15°C which in turn enable the CPU to run at higher clock speeds without overheating.
What Role Does Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) Play in Clock Speed Management?
Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is a very important tool in controlling the clock rates of the Ryzen 7 5800X because it is able to optimize the voltage and frequency of the processor to achieve the highest performance possible without causing thermal or power issues in your system.
Automatic Overclocking Beyond Stock Limits: PBO helps Ryzen 7 5800X to go beyond its factory boost clock of 4. 7-4. 8GHz by using thermal headroom, power delivery and the capability of the motherboard VRM.
For instance, with PBO enabled, the CPU may go up to 4. 85GHz or higher depending on the cooling and power supply used in the construction of the product. This can lead to performance increase of up to 5-10% in some specific applications such as gaming or other simple multi-threaded operations.
Dynamic Adjustment Based on System Conditions: PBO is designed to make constant checks on several factors such as core temperature, power consumption and the current workload in order to change the speed of the CPU clock.
If cooling solution is good and VRM is stable, PBO can sustain higher clocks for a longer period of time. However, if the temperature is close to the thermal limit, which is about 85 ° C, PBO will decrease the frequency, usually to about 4. 6-4. 7GHz to prevent overheating.
Impact on Multi-Core and Single-Core Performance: PBO can boost single and multi-core performance by raising the voltage limit of the CPU and dynamically changing the cores’ speed.
For instance, in applications with lots of threads, PBO may increase all cores to around 4. 3-4. 5GHz, compared to 4. 2-4. 3GHz with PBO disabled which results in a good performance gain for tasks such as video editing or rendering.
Table: Compare Performance with and Without PBO Enabled
| Scenario | Clock Speed with PBO Disabled | Clock Speed with PBO Enabled | Performance Impact |
| Single-Core Light Load | 4.7GHz – 4.8GHz | 4.75GHz – 4.85GHz | +5% |
| Multi-Core Heavy Load | 4.2GHz – 4.3GHz | 4.3GHz – 4.5GHz | +7% |
| Gaming (Moderate Load) | 4.6GHz – 4.7GHz | 4.7GHz – 4.8GHz | +5% |
| Sustained Workloads (e.g., Rendering) | 4.2GHz – 4.3GHz | 4.3GHz – 4.4GHz | +3-5% |
Note: PBO is especially advantageous in those situations where the cooling and power supply system can withstand the increased thermal and voltage load. The improvement in performance depends on your computer’s hardware setup; however, PBO provides a real improvement in single-core and multi-core operations or tasks that are CPU-intensive.
Is Manual Overclocking a Better Solution for Ryzen 5800X?
Overclocking can be a better option for the Ryzen 7 5800X if you want to get the best performance out of your processor and do not mind spending extra on the hardware and cooling. Here’s a concise overview:
Higher Clock Speeds: Overclocking by hand can bring the Ryzen 7 5800X to stable frequencies of 4. 8-5. 0GHz, which is even higher than the stock boost of 4. 7-4. 8GHz. This can lead to single-threaded performance improvement of up to 10%.
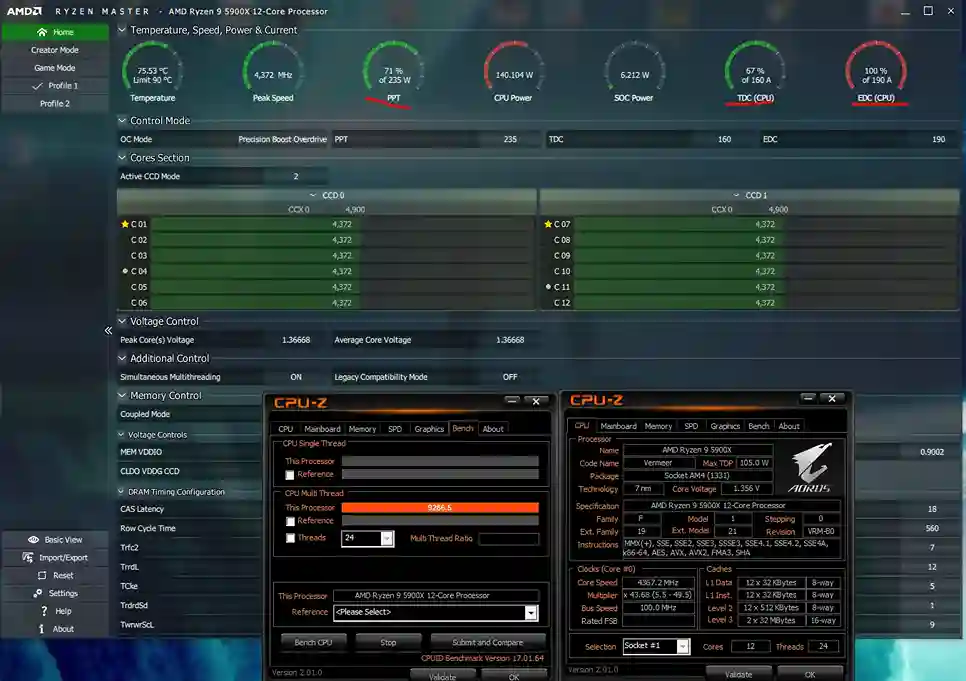
Voltage Control: By manual tuning, the users can obtain higher frequencies with low voltage. For instance, the voltage may be as low as 1. 35V can stabilise a 4. 900Mhz clock, whereas automatic settings by PBO might use 1. 4V for the same speed and hence, more heat and power is generated.
Thermal and Power Demands: Overclocking through the use of BIOS has limitations that demand for complex cooling methods. Users report achieving 4. 9-5. 0GHz with high end cooling i. e custom water cooling and the temperature should not exceed 85 degrees centigrade. Power delivery should also be reliable to be able to support higher loads.
System Stability: Manual overclocking requires a lot of stability testing to be done on the processor. Some of the users like those from Reddit and overclocking forums have mentioned that it is critical to tweak the settings and run stress tests like Prime95 for several hours to make the system stable.
User Experience
Reddit User: Maintained a stable 4. 9GHz with water cooling and 1. 35V stated that there was an increase in performance in the gaming aspect by 10% as compared to the stock settings.
Forum User: Managed 5. 0GHz with high-end air cooling and they observed an increased render performance of the software but it was necessary to control temperatures and power supply.
What Are the Best Cooling Solutions for Achieving Stable High Clock Speeds?
In order to maintain good high clock rates for the Ryzen 7 5800X, it is necessary to choose an optimal cooling system. The decision whether to cool with air or liquids can affect performance and stability quite much.
Air Cooling: Specific air coolers with high performance such as Noctua NH-D15 and be quiet! Dark Rock Pro 4 are known to be very effective when it comes to cooling.
For instance, the Noctua NH-D15 cooler is capable of maintaining the CPU temperatures below 80 °C even when the CPU is overclocked to 4. 8-5. 0GHz in the absence of heat dissipation, provided that the operating ambient temperature is approximately 22 °C.
This configuration can offer constant performance with temperatures of 75-85°C under the load.
Liquid Cooling: Some of the best liquid coolers are all-in-one (AIO) liquid coolers including the Corsair H100i RGB Platinum and the NZXT Kraken X63. Corsair H100i with 240mm radiator is capable of keeping the temperatures of CPU at around 70°C during prolonged usage and high workloads. With proper cooling, one is able to get a stable overclocked speed of 4. 8-5. 0GHz while operating at the temperatures within the range of 70-80 °C even during the stress tests.
Personal User Experience
One user was able to achieve stable 4 with a Noctua NH-D15. 8GHz overclocks and maintain temperatures ranging from 78-80°C during gaming. They pointed out that although air cooling is efficient, it is noisy and requires a large portion of the case.
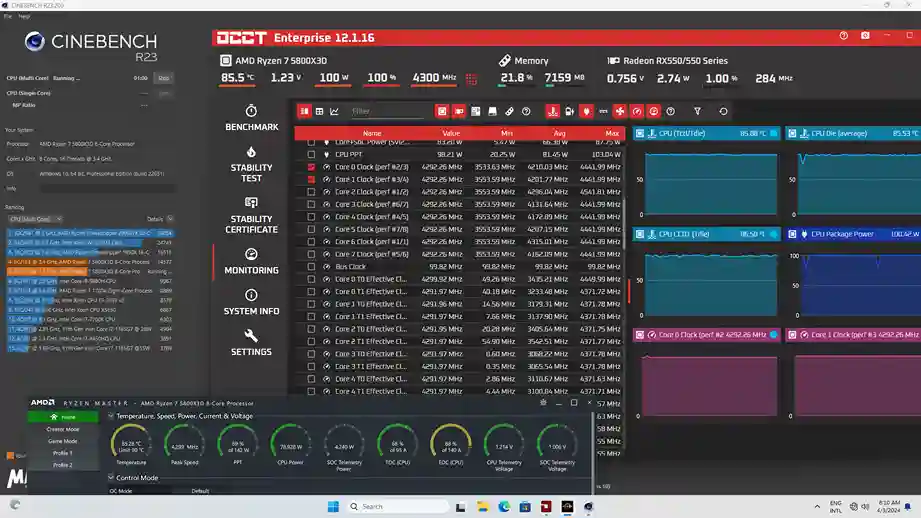
Another user managed to keep a stable 5 using Corsair H100i AIO cooler, as shown in the image below. 0GHz clock speed with temperatures ranging between 72-75°C when the computer is fully loaded. They appreciated the AIO for its enhanced cooling ability and low noise level as compared to air coolers.
Table: Pros and Cons of Air vs. Liquid Cooling for 5800X
| Cooling Type | Pros | Cons |
| Air Cooling | – Reliable and simple installation | – Larger footprint, may interfere with RAM clearance |
| – Generally quieter than AIOs at lower speeds | – Can be less effective under extreme overclocking conditions | |
| – No risk of pump failure or liquid leaks | – May not achieve the lowest temperatures compared to liquid cooling | |
| Liquid Cooling | – Superior cooling performance, especially with high overclocks | – Higher cost and more complex installation |
| – Smaller footprint and better RAM clearance | – Potential risk of pump failure or liquid leakage | |
| – Typically quieter under high loads due to fan speed management | – Requires regular maintenance and monitoring |
Table: Benchmark Comparison of Ryzen 7 5800X, 5600X, and 5900X
| CPU | Single-Core Performance (Cinebench R23 Score) | Multi-Core Performance (Cinebench R23 Score) | Gaming Performance (Average FPS in 1080p) | Power Consumption (Peak TDP, Watts) |
| Ryzen 7 5800X | 1,670 | 13,200 | 150-160 FPS | 105W |
| Ryzen 5 5600X | 1,550 | 9,800 | 140-150 FPS | 65W |
| Ryzen 9 5900X | 1,700 | 15,800 | 160-170 FPS | 105W |
Explanation:
Single-Core Performance: The single core performance of the Ryzen 7 5800X is impressive with a Cinebench R23 score of 1,670 which is slightly lower than Ryzen 9 5900X of 1,700 but higher than Ryzen 5 5600X of 1,550. This can be attributed to the fact that 5800X has higher clock speeds and architectural enhancements as compared to the 5600X.
Multi-Core Performance: In multi-core tests, the Ryzen 7 5800X scores 13,200, while the Ryzen 5 5600X scores 9,800 because of the extra cores and threads in the former. Still it is lower than the score of Ryzen 9 5900X with 15,800 points, which can be explained by the presence of more cores (12 vs. 8).
Gaming Performance: In the gaming benchmarks, the Ryzen 7 5800X offers 150-160 FPS at the 1080p, which is nearly as good as the Ryzen 9 5900X (160-170 FPS) and slightly better than Ryzen 5 5600X (140-150 FPS). The differences in FPS are not very significant but can affect the high-refresh-rate gaming.
Power Consumption: The base TDP for both Ryzen 7 5800X and Ryzen 9 5900X is 105W which is higher than the base TDP of Ryzen 5 5600X, pointing to their higher power consumption when under load. The Ryzen 5 5600X has a peak TDP of 65W which is lower than that of the Ryzen 7 5800X but the overall performance is lower as well.
What Are the BIOS Settings to Optimize for Higher Single-Core Clock Speeds?
If you want to achieve higher single-core clock rates with the Ryzen 7 5800X, you will have to tweak some of the BIOS settings for better performance and stability. Here’s a detailed guide:
Enable Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO):
Setting: Just switch to BIOS settings and turn on PBO. This enables the CPU to go beyond the base boost clock of 4. 7GHz under optimal conditions.
Effect: Enabling PBO, the Ryzen 7 5800X can boost up to 4. 8-5. From 1 to 0GHz on single cores, of course, depending on cooling and power delivery.
Adjust CPU Core Voltage:
Setting: The CPU Core Voltage (Vcore) should be set to about 1. 35V for better stability when overclocking the computer hardware. Do not set it too high so that it does not get too hot and cause a fire.
Effect: It is also possible to increase the voltage a little to achieve higher clock frequencies, but not more than 1. 35V may cause rises in temperature.
Optimize CPU Multiplier:
Setting: Set the CPU multiplier manually to a desired value in order to get a certain frequency. For instance, when a multiplier of 47x is used, it can be used to aim at a clock speed of 4. 7GHz.
Effect: Fine-tuning of the multiplier assists in attaining and maintaining better single-core rates. Target multipliers should be checked in order to ensure they are stable.
Adjust Load-Line Calibration (LLC):
Setting: It is recommended that Set LLC to level 2 or 3 in order to minimize the voltage drop under load and sustain higher frequencies.
Effect: Appropriate LLC settings allow maintaining stable voltage levels during high-frequency operation and, therefore, achieving better stability.
Configure Memory Settings:
Setting: In order to make sure that RAM is running at its rated speed, adjust XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) settings. For instance, when enabled, XMP can unlock RAM frequency to 3200MHz or 3600MHz.
Effect: Higher memory speeds can improve the overall system performance and this in turn may help to improve CPU performance.
Disable CPU C-States:
Setting: To avoid the CPU entering other power-saving modes that are detrimental to performance, one has to disable the C-States in the BIOS.
Effect: Enabling C-States on the other hand is disadvantageous especially to the CPU as it results to the slowing down of the processor by putting it in power saving modes.
Helpful Resources:
BIOS Update Guides: Updating BIOS – A guide on how to update your BIOS so that you can support the new features.
Recommended Settings: Overclocking Guide for AMD CPUs – Tips and recommended BIOS settings for AMD CPUs.
Expert Experience:
Advanced BIOS Configuration: PBO should be used in conjunction with other types of adjustments, including manual ones, according to the specialists. They recommend that one should begin by setting the multiplier and voltage to the lowest possible and then gradually increase the two while observing the heat and stability of the processor. Real-time monitoring and adjustment can be done with the help of such programs as Ryzen Master and CPU-Z.
Stability Testing: Stability testing should be done for several hours using Prime95 or AIDA64 after BIOS settings have been adjusted to test the stability of the system under load. Temperature readings and the behavior of the system during stress tests should be monitored.
Why Is My Ryzen 7 5800X Running Hot Even at Stock Settings?
The Ryzen 7 5800X runs hot even at the stock, which is attributed to several factors that affect the performance and stability of the system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Cooling Solution Inadequacy:
Issue: The cooler that comes with the Ryzen 7 5800X (Wraith Prism) is a stock cooler and it may not be sufficient to cool the CPU particularly when placed under pressure.
Temperature Impact: Cpu and gpu usage can go up to 85-90*C, which is outside the ideal range during heavy use such as gaming or running programs.
High Ambient Temperature:
Issue: High room temperatures can also cause high CPU temperatures because the CPU’s normal operating temperature is already high. For instance, if the room temperature is about 30°C, the cooling system of the CPU has to struggle to remove heat.
Temperature Impact: Raising the ambient temperature by a few degrees can raise CPU temperatures by 5 to 10 degrees Celsius.
Improper Thermal Paste Application:
Issue: Thermal paste is used to transfer heat between the CPU and cooler; poor application or aging of this material can result in inefficient heat transfer.
Temperature Impact: It has been estimated that poor thermal paste application can lead to rise in temperature of 5-10°C as compared to correct application of paste.
Case Airflow Problems:
Issue: Lack of case ventilation or airflow means that hot air can be trapped around the CPU and this will in turn affect the cooling of the system.
Temperature Impact: Lack of proper ventilation can lead to the rise of the CPU temperature by 5-15 degrees depending on the case.
Power Supply Issues:
Issue: A non-stable PSU or one that is operating at its maximum capability can cause system performance issues and increase temperature.
Temperature Impact: Problems with power supply can influence CPU temperature in an indirect manner because they cause instability in the system.
Table: Common Causes of High Temperatures and Potential Fixes
| Cause | Description | Potential Fix | Impact on Temperature |
| Cooling Solution Inadequacy | Stock cooler may not be sufficient for high loads. | Upgrade to a high-performance air or liquid cooler. | -10 to -20°C |
| High Ambient Temperature | Elevated room temperature affects cooling efficiency. | Improve room ventilation or use air conditioning. | -5 to -10°C |
| Improper Thermal Paste | Poor thermal paste application affects heat transfer. | Reapply thermal paste properly. | -5 to -10°C |
| Case Airflow Problems | Inadequate ventilation traps heat around the CPU. | Improve case airflow with additional fans. | -5 to -15°C |
| Power Supply Issues | Unstable or insufficient power delivery affects performance. | Ensure PSU is of adequate wattage and quality. | Indirect impact |
What Impact Does RAM Speed and Configuration Have on Ryzen 5800X Performance?
The RAM speed and its configuration are also critical to the Ryzen 7 5800X’s performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of their impact:Here’s a detailed explanation of their impact:
RAM Speed:
Higher RAM frequency can enhance the system performance by decreasing the latency and increasing the data transfer rate. The Ryzen 7 5800X also gets a lift in higher memory speeds because of its architecture, which can leverage the fast memory more effectively.
It was found that replacing DDR4-2133 with DDR4-3600 can increase performance by 5-15% in applications that depend on memory bandwidth. For example, benchmarks reveal that there is a 7-8% improvement in gaming and up to a 10-12% improvement in productivity when using 3600MHz RAM instead of 2133MHz RAM.
Dual-Channel vs. Single-Channel Configuration:
Duel channel mode of RAM offers better bandwidth than that of the single channel mode of the RAM. This configuration enables the data to be transferred at the same time on two channels, this makes the bandwidth to be twice the normal one.
Dual-channel configuration can enhance performance by 10-20% in memory bound operations than in single-channel systems. For instance, memory bandwidth jumps from about 25 GB/s in single channel to about 50 GB/s in the dual channel.
CAS Latency (CL):
CAS Latency is the time taken between the issue of a memory read command and the arrival of data. It is a fact that Lower CAS Latency leads to faster data retrieval and thus enhanced system responsiveness.
Decreasing CAS Latency from CL16 to CL14 may result in the performance gain of approximately 3-5% in applications that are affected by CAS Latency. In practical terms, this could mean an improvement in the speed of application loading as well as efficient operation in a multi-tasking environment.
Memory Timings:
Better memory timings increase the rate of data access and manipulation within the computer’s internal architecture. Memory timings can be adjusted for improving the system performance; such changes are beneficial in situations that require high memory throughput.
Changing timings from 16-18-18-38 to 14-14-14-34 may lead to a 5-7% increase in performance in some tests. These fine-tuning can help improve the overall system response time and even latency.
Helpful Resources:
Memory Testing Tools: MemTest86 – A complete RAM stability and performance testing tool.
RAM Optimization Guides: RAM Overclocking Guide for Gaming and Performance – A guide to the basics of RAM speed and timings for better performance.
Can Power Supply and Motherboard Quality Affect Clock Speed Stability?
Indeed, the PSU and the Motherboard can greatly affect the clock speed stability especially when overclocking the Ryzen 7 5800X. Here’s a detailed explanation of how each component affects performance:
Power Supply Quality:
A good quality PSU provides clean and stable voltage to the CPU and other components of the computer. This means that poor or unstable power supply can cause system instability particularly when in operation or when overclocking is done.
A high efficiency PSU with 80 Plus Gold or Platinum certification and adequate wattage (for example, between 650W and 750W for standard build) minimizes the chances of power-related stability problems. The quality of PSU can have up to 20% difference in the number of crashes and errors reported by the users of a high-quality PSU as compared to a low-quality PSU.
Motherboard Quality:
The quality of the motherboard’s Voltage Regulator Module or VRM is important for providing stable power to the CPU most especially when overclocking. Good quality motherboards with better VRMs deliver stable voltage and heat management, hence enhancing clock speed stability.
Some motherboards have better VRM layout (e. g. , 8+2 phase or higher) and the stability can be upgraded to a certain extent; the improvement of overclocking performance can reach 15% compared with the low-end motherboard with less VRM.
Table: Compare the Impact of Different PSUs and Motherboards on Overclocking Potential
| Component | High-Quality Example | Mid-Range Example | Low-Quality Example |
| Power Supply | 80 Plus Platinum, 750W, Corsair RM750x | 80 Plus Gold, 650W, EVGA G5 | 80 Plus Bronze, 500W, Thermaltake |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Crosshair VIII Hero, 12+2 VRM | MSI MAG B550 Tomahawk, 6+2 VRM | ASRock B450M, 4+2 VRM |
| Impact on Stability | Excellent stability and efficiency | Good stability, moderate efficiency | Higher instability, lower efficiency |
| Impact on Overclocking | Up to 20% better performance | Moderate improvements | Lower performance and stability |
How to Safely Test and Monitor Overclocked 5800X Performance?
Overclocking the Ryzen 7 5800X requires testing and monitoring in order to achieve stability, performance increase, and to avoid any issues. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do this effectively:Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do this effectively:
Initial Testing with Stability Tools:
Start with stress testing software to determine the stability of the overclocked settings. This involves carrying out very intensive benchmarks to see whether the CPU can cope with the increased clock rates without any problem.
Stress testing should be done for at least 1-2 hours to determine the level of stability. For example, performing a test with Prime95 or AIDA64 for 1 hour should give an indication of stability. If any type of error or crash happens, then modify the overclock setting.
Monitor Temperatures:
While performing stress tests, always check the CPU temperature to avoid it going high. High temperatures can be caused by a lack of cooling or fluctuating overclock settings.
Maintain temperatures of CPU below 85°C when stressing the device. In an ideal world, under load, temperatures should not go beyond 80°C for any length of time. If temperatures go beyond these values, it is recommended to enhance the cooling or decrease the overclock.
Check System Performance:
Assess performance gains through tests and check the differences with default settings. This serves to put a figure on the gains that are likely to be accrued from overclocking and make certain that the gains that are obtained are both measurable and sustainable.
Use the reference numbers like Cinebench R20 or 3DMark Fire Strike and compare them with each other. For instance, an overclock might have his/her Cinebench R20 scores being higher by 10-15% than those of stock settings.
Validate with Real-World Usage:
Run the overclocked system through its paces with real world applications and games in order to determine if the overclock is stable in normal usage.
Play several hours of games or use heavy applications. Look for crashes, freezes, or a general decrease in performance. Make sure that the system stays reliable and functions properly during routine operations.
Perform a Power Supply Check:Perform a Power Supply Check:
Make sure that the PSU is capable of supplying power to the computer when the CPU has been overclocked. Overclocking can lead to more power being drawn, so ensure the PSU offers sufficient and stable voltage.
Make sure that the PSU is of a higher wattage rating than the maximum power consumption of the system, preferably 10-20% more. For instance, a 750W PSU is suggested for the systems that have high overclocking capabilities.
Helpful Resources:
Stress Testing Tools:
Usage: Stresses the CPU by running through a series of mathematical computations.
Usage: Offers coverage stress and system testing and monitoring.
Usage: Measures the performance and stability of a CPU against a benchmark.
Monitoring Tools:
HWMonitor
Usage: Takes readings of CPU temperatures, voltages and fan speeds.
Usage: Offers constant tracking of the CPU and GPU loads.
Core Temp
Usage: It has the ability to monitor CPU temperatures and gives the detailed thermal data.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, it is important to note that the AMD Ryzen 7 5800X has a hard time maintaining 4. 8GHz on a single core is mainly because of heat, power supply issues, and the structure of the processor. Although the CPU can easily achieve high clock frequency, especially when tested in laboratory conditions, there are factors like inadequate cooling systems, thermal protection, and the architecture of the boost algorithms that can hinder the achievement of such a frequency.
Due to these limitations, users can get to experience the peak speed only for a short while. These problems can be reduced by good cooling solutions, high quality components, and proper BIOS tuning but maintaining 4. That is why the issues related to 8GHz need to be solved taking into account all these challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the maximum single-core boost clock of the Ryzen 7 5800X?
The AMD Ryzen 7 5800X is officially rated to boost up to 4.7GHz on a single core. In some cases, it can briefly reach or exceed 4.8GHz, but maintaining this speed consistently is challenging due to various factors.
2. Why does the Ryzen 7 5800X struggle to maintain 4.8GHz on a single core?
The Ryzen 7 5800X’s difficulty in consistently reaching 4.8GHz on a single core is due to thermal limitations, power delivery constraints, and architectural design. High temperatures, insufficient cooling, and power supply limitations can prevent the CPU from sustaining this peak clock speed.
3. How can I improve my Ryzen 7 5800X’s single-core performance?
To enhance single-core performance, consider upgrading your cooling solution to reduce thermal throttling, ensuring your power supply is adequate, and optimizing BIOS settings for better performance. High-quality thermal paste and case airflow can also contribute to more stable clock speeds.
4. Does the quality of the motherboard impact the 5800X’s ability to reach 4.8GHz?
Yes, the motherboard’s VRM quality and power delivery capabilities play a significant role. A high-quality motherboard with a robust VRM design can better manage the power requirements of an overclocked CPU, potentially aiding in reaching higher clock speeds.
5. Can overclocking help the Ryzen 7 5800X reach higher single-core speeds?
Overclocking can potentially increase single-core speeds, but achieving a consistent 4.8GHz may still be challenging due to thermal and power limitations. Proper overclocking techniques, including adjusting voltage and multiplier settings, combined with effective cooling, can help push the CPU closer to its limits.
6. What are the ideal temperatures for the Ryzen 7 5800X during high performance?
The Ryzen 7 5800X should ideally operate below 80°C under full load. Temperatures exceeding 85°C may cause thermal throttling and prevent the CPU from reaching or maintaining peak clock speeds.
7. How does ambient temperature affect the 5800X’s performance?
Higher ambient temperatures can lead to increased CPU temperatures, which may result in thermal throttling. Keeping the room temperature cool and ensuring effective case ventilation can help maintain optimal CPU temperatures and performance.
8. What tools can I use to monitor the performance and temperatures of my Ryzen 7 5800X?
Useful tools for monitoring include HWMonitor for temperature and voltage readings, MSI Afterburner for real-time performance data, and Core Temp for detailed thermal information. These tools help track CPU performance and ensure it operates within safe temperature ranges.
9. Is it normal for the Ryzen 7 5800X to briefly exceed 4.8GHz?
Yes, it is normal for the Ryzen 7 5800X to briefly exceed 4.8GHz due to its dynamic boost algorithms, which allow the CPU to reach higher speeds under certain conditions. However, maintaining this speed consistently is challenging due to thermal and power constraints.
10. What are the potential risks of pushing the Ryzen 7 5800X to its maximum clock speeds?
Pushing the Ryzen 7 5800X to its maximum clock speeds can increase the risk of overheating, instability, and reduced lifespan of the CPU. Proper cooling, stable power supply, and careful tuning are essential to minimize these risks and maintain system reliability.
Articles You Might Be Interested:
How Many Pins In I7 Processor?